The potential impact of chat on SEO and publisher: A Three-Month Retrospective
In just three months, every major search engine now has AI chat integrated—and with ChatGPT's new internet access and plugins, the game has changed for SEO.
This post was written in 2023. Some details may have changed since then.
Three months ago, I wrote about the potential impact of chat on Paid Search and SEO. Since then, things have moved fast. So here's my update on what's happened and what I think it means — especially for publishers and anyone doing SEO.
Key developments since my February article
Google officially introduced chat in Google Search
During Google I/O on May 10, Google officially introduced generative AI for Google Search. With this announcement, all the biggest search engines in the world (including Bing and Baidu) now have generative AI as part of the search experience.
ChatGPT can now browse the internet
On May 12, OpenAI announced that Web browsing and Plugins are now rolling out in beta. This is a big deal for a number of reasons. One of them is the fact that chatGPT can now access the internet in real-time. Previously, one of the main barriers to using chatGPT to search was that it could not access the internet and the training data set was last updated in late 2021.
and chatGPT does a lot more things
Also, with plugins, chatGPT now has a lot more functionalities, including completing certain commercially valuable tasks like booking a trip.
If you haven't tried these combined functionalities from chatGPT yet, let me show you an example
- Previously, without the ability to browse the internet and use plugins, I would not go to chatGPT to learn more about Yuval Harari's latest talk at the Frontiers Forum "AI and the future of humanity".
- chatGPT doesn't have the latest information and this talk was on May 14, 2023.
- It couldn't summarize the content right in the chat interface well and I had to use other Chrome plugins (like chatGPT for YouTube) to summarize the Youtube content for me.
- Now, with plugins, I can go to chatGPT and just do this:
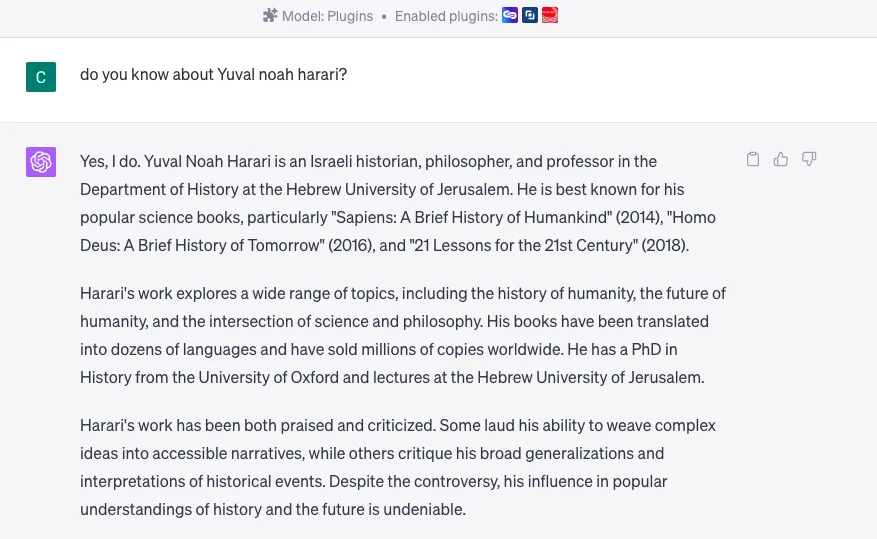
- "Do you know about Yuval Noah Harari?" ChatGPT will give me the answer with a high-level introduction about Yuval.
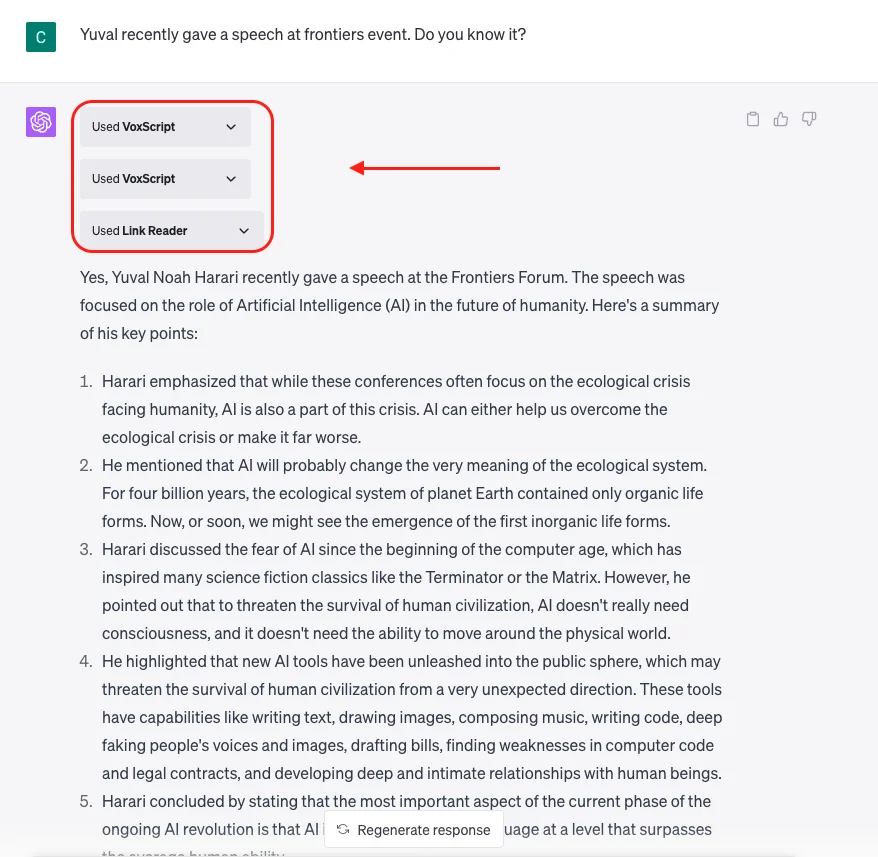
- Then I can ask "Yuval recently gave a speech at Frontiers event. Do you know it?"
- And then chatGPT tells me that it knows about the talk and automatically gives me the summary of the talk.
- chatGPT automatically knows that it should use "VoxScript" and "Link Reader" plugins without me telling it to do so. Brilliant!
- Below are the screenshots of what chatGPT dose
Microsoft announced the next wave of AI innovation with Microsoft Bing and Edge on May 4
Bing Chat is now open to everyone across the globe. A big caveat is that you need to use the Microsoft Edge browser or the Bing App to experience all the functionalities. But you can do a lot more now with Bing Chat including
- Generating AI images right there on Bing chat
- Use Edge Copilot to help you to summarize the content of the web page that you are on
- Use Bing actions/ Edge actions to complete certain tasks. This is very similar to chatGPT Plugins.
So what does this all mean for publishers, for SEO?
(Quick caveat before we go into this topic. If you watch the latest talk from Yuval above, his main narrative is about "AI mastering language can manipulate and generate stories, laws, policies, and tools, which can shape human culture. AI could eat up the whole of human culture, ending human-dominated history." So in a way, there are many bigger fishes to fry vs. trying to answer this topic :D ) Now back to the topic of this post.
Impact on Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
- The cost and effort to generate content will become lower over time. This is not limited to text but to images, video, and audio (podcast) too. It means it will be easier, faster, and cheaper over time to achieve topical authority.
- When everyone starts doing it, it will mean that comparative advantages will be erased.
- As generative AI is getting better and better at images, video, and audio, the comparative advantage of having multiple content formats will go away too. I anticipate this will happen in the mid-term.
But what about the return? if SEO is driving less traffic to the website because people can get the direct answer from chat then what is the point of doing SEO?
To answer this question, it may be helpful to look at different types of search queries. Generally, the common types are:
- Navigational searches: This type is pretty straight forwards. Users have a specific website in mind but just don't remember the exact URL, they type something in the browser to find the URLs and that's it. For example, users may type in "WSJ" because they are looking for Wall Street Journal website or app.
- I don't think people will use generative AI/chat to complete navigational searches.
- Doing basic SEO so that your website appears for your brand name continues to be fundamental but it won't take much effort.
- Informational searches: These are used when a user is looking for information. This could be a simple fact, a detailed explanation, advice, tutorials, and so on. Examples could include "how to bake a cake" or "history of the Roman Empire". These keywords often start with "how to", "what is", "why does", etc. For this type of query, there can be two broad scenarios:
- When accuracy is critical or important like drug dosage, or serious health-related queries, until generative AI can get to a much higher level of accuracy, I don't think people will use it for this purpose. So doing SEO is important here.
- When users don't need a high level of accuracy or don't mind fact-checking occasionally, which includes a lot of common situations, they will use generative AI and immediately get the answer. For example, my daughter Sophie started baking at home recently and she just entered once in chatGPT "what is the best chocolate chip cookie recipe" and then followed the instructions there. It worked out pretty well :D
- Transactional keywords: These are used when a user is ready to make a purchase or perform some other specific action. They might include terms like "buy", "order", "sign up", or "download". For example, "buy iPhone 12" or "order pizza online".
- First of all, for many common product categories, users are already going direct to a particular app to complete their purchases like Amazon, Walmart, or Hyatt, United Airlines, etc...
- With chatGPT plugins, Bing/Microsoft Actions, I actually think that over time, many of these transactions will be completed by these plugins. The flow is a lot more intuitive since users are already doing informational searches using generative AI.
- So doing SEO for this keyword category may not continue to have a long-term benefit.
- Commercial Investigation keywords: These are used when a user is looking to make a purchase but is still in the research phase. They might be comparing products, looking for reviews, or seeking the best place to make their purchase. Examples could include "best DSLR cameras" or "iPhone vs. Samsung".
- My educated guess is that people will use generative AI search for this type of keyword.
- So again, doing SEO here might not make sense long term
- Local keywords: These are used when a user is looking for something within a specific geographical area. For example, "Italian restaurants in New York" or "car repair service in Austin".
- This is where I think Bing chat or chat in Google Search will do really well because they already have a lot of information about local businesses via Map, reviews, etc... ChatGPT may not do as well in this particular area, even with plugins.
- Doing SEO for this type of keywords may help both searches using generative AI and traditional search.
So what is my conclusion here? Unfortunately, it is likely that the return on the effort of doing SEO will decrease in the medium to long term across many keyword categories.
From an end-user perspective, this will help to clean up content farms and reduce lower-quality content over time. SEO will be less about optimizing for search engines but about optimizing the actual answers for humans.
Impact on publishers
Having a distinctive brand, and direct relationship with your readers will become even more important because:
- It will motivate your loyal readers to go to your website/app to read, listen, watch, and interact with your brands
- You will not be at the mercy of any generative AI search algorithm because users know your brand. And as long as the content is good and your content distribution channels are open, they can find you and engage with you.
But generating great content is often costly (in time, effort, and money). So how can publishers survive (let alone thrive)? I don't know the answer here beyond the obvious like:
- Advertising is not the solution for a medium or big publisher.
- Subscription is not easy to scale. And even at large scale (like the NY Times), it is still not a big business in comparison to other industries
- You may need to try indirect ways of monetizing the traffic you have, depending on the particular niche that you are in.
That's it from me. I might be wrong about some of these predictions — the space is moving so fast that what I wrote above could be outdated in a few months. But from my experience in digital marketing over the past 18 years, I think the directional shift is real.
What do you think? Are you already seeing changes in how your audience finds content? I'd love to hear your perspective.
Cheers,
Chandler
P.S. A quick summary of the talk by Yuval about "AI and the future of humanity" is below in case you are curious. The summary was written by chatGPT for Youtube plugin. I checked the summary quality and it is really good.
AI mastering language can manipulate and generate stories, laws, policies, and tools, which can shape human culture. AI could eat up the whole of human culture, ending human-dominated history.
- AI has gained mastery of language surpassing the average human ability.
- AI can exploit with superhuman efficiency, the weaknesses, biases, and addictions of the human mind.
- The sacred texts of future religions and cults could be written by non-human intelligence, with far-reaching consequences.
- Lengthy online discussions could take place with bots that may appear to be human, but actually, they are programmed AI bots.
- AI can form intimate relationships with people to influence their opinions, thoughts, and feelings.
- The entire advertisement industry could collapse as humans use AI to get information.
- AI could eat up the whole of human culture, ending human-dominated history.